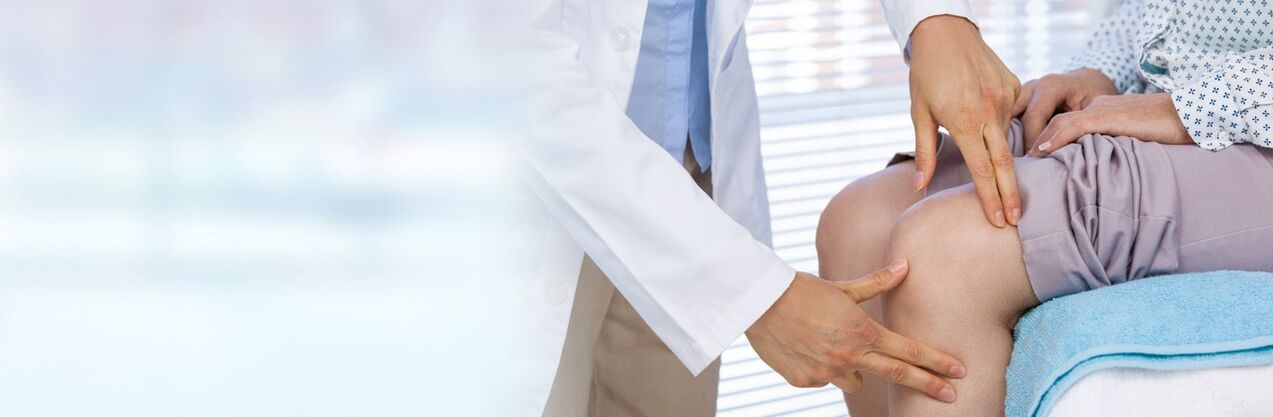
Types of arthrosis of the knee joint
primary knee arthropathy
- Natural degeneration or degeneration due to slowing of metabolic processes in the body;
- being overweight;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- malnutrition;
- Genetic susceptibility.
secondary arthropathy
- Various injuries - ligament or meniscus bruises, fractures, dislocations, ruptures and sprains;
- Joint diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, osteochondritis dissecans, gout, knee arthritis, etc. ;
- local vascular disease;
- Overloading of the knee joint during exercise or due to the specific circumstances of the job;
- endocrine diseases;
- O-shaped and X-shaped curvature of the legs.
Stages and symptoms of knee arthritis
Stage 1– Mild pain that occurs after prolonged exercise, when climbing stairs, or after strenuous exercise, and disappears after rest. Movement is not restricted, but slight swelling of the joints may sometimes occur. If nothing is done, this condition can continue for years - when the cartilage is just beginning to lose its smoothness due to compromised blood supply. X-rays will show slight narrowing of the joint space and hardening of the bones. - second stage– Pain can become severe and last for a long time even with slight exertion. A crunching sound may be heard when the joint is flexed and extended. Unable to fully bend the leg due to severe pain. There is slight deformation, muscle atrophy and limited mobility. The pain may be relieved with painkillers or may go away on its own with rest.
At this stage, the cartilage layer has become greatly thinned and even disappeared in some places. The synovial fluid becomes thicker and more viscous, which compromises its nutritional and lubricating properties. Osteophytes - bone growth - appear. - The third phase– The pain increases and is constantly worrying, even at night. Joint deformities become apparent, gait changes, and the lower limbs bend. Reduced range of motion in the knee joint - the leg cannot fully bend or straighten. When walking, you must use a support such as a stick or crutches. Painkillers no longer help.
Cartilage is almost completely lost, bones are compacted, and joint space is greatly reduced or eliminated. The presence of numerous osteophytes was noted.
diagnosis
Treatment of knee arthritis
- relief the pain;
- Prevent pathological progression;
- Restore joint function.
Conservative treatment of knee joint disease
- Shock wave therapy – the use of low-frequency, significant amplitude sound pulses to produce short-term effects on bone and connective tissue;
- Electrotherapy – exposure of affected areas to electrical current, magnetic or electromagnetic fields;
- Laser therapy – exposure to light radiation produced by a laser;
- Phonophoresis – irradiating the affected area with ultrasound waves and applying medication to the skin;
- Electrophoresis - Exposing the affected area to an electric current.
Minimally Invasive Methods for Treating Knee Arthropathy
- Hyaluronic Acid – Acts as a replacement for synovial fluid to improve friction, reduce pain, and improve knee joint function. The average duration of action of the drug is 3-6 months;
- Platelet-rich autologous plasma - for nutrition and repair of cartilage tissue;
- Corticosteroids – Reduce inflammation.
Surgical methods for treating knee joint disease
- Arthrodesis – Artificial immobilization of affected joints in physiological positions to eliminate pain;
- Arthroscopic debridement – the use of an arthroscope to clean the joint;
- Corrective osteotomy – the elimination of skeletal deformities through artificial fractures;
- Endoprosthesis – Replacing a worn joint with an artificial implant made from biocompatible materials.
complication
- Persistent pain that cannot be relieved by medication;
- Affected joints are completely immobile;
- Unable to rely on injured limb;
- The leg joints are severely deformed and bent;
- Damage to other parts of the musculoskeletal system;
- The legs are shortened.
prevention
- Make sure your weight is within age limits;
- Don’t engage in sports that put excessive pressure on your knee joints;
- If possible, cure infectious diseases completely without causing complications;
- Don’t become too cold or overtired;
- Avoid joint injuries and overload;
- avoid stressful situations;
- Don’t forget to take breaks;
- Perform exercise therapy;
- Wear orthopedic shoes.
FAQ
- What is the difference between knee arthritis and knee arthrosis?
Arthritis is a general term for joint inflammation, and arthrosis is a degenerative dystrophic process. - Which doctor treats joint disease?
Traumatologist - Orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist. - Can I still participate in sports if I have arthritis in my knees?
The joints should be protected from prolonged heavy loads and axial impacts. But you shouldn't completely cut exercise out of your life - your joints are better "nourished" and restored when you move. It is important to observe the measurements and follow the recommendations of your doctor, who will choose the type and mode of exercise.